biot savart law:definition, examples, problems and applications
What is the definition of biot savart law?
Biot Savart law is defined as: “The magnetic induction at any point produced by current element is directly proportional to the product of the current and the differential element and inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the differential element.”
Derivation of Biot Savart law

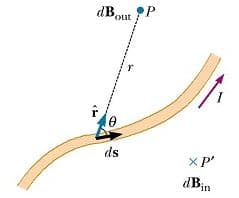
To explain the Biot Savart law, we consider a point near a wire carrying current i. Let ds be an element of the length of wire and dB be the magnetic induction produced by this length element at a distance r from the current-carrying wire. It is found that:
1:The magnitude of magnetic induction dB is proportional to the current i.
dB ∝ i
2:The magnitude of magnetic induction dB is directly proportional to the current dsSinθ
dB ∝ dsSinθ
3:The magnitude of magnetic induction dB is inversely proportional to r².
dB ∝ 1/r²
By combining the above three relations we have:
For Related Topic visit our page: Electricity and magnetism
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…