Boiling Point of Water: The Definitive Guide ( 2020)
This is the Ultimate Guide in which you will learn about:
- What is boiling?
- Boiling Point Definition
- Factors affecting on Boiling
- Examples of the boiling point of Different substances
- Frequently asked related questions
If you want to get benefits from this guide, you’ll love this guide.
Let’s dive right now…
What is Boiling?
Boiling is the rapid vaporization process of liquid, which happens when the liquid is heated at its boiling point, which is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding atmosphere. There are two basic types of boiling, critical heat flux boiling and nucleate boiling. Transition boiling is intermediate with the elements of both types. The boiling point of water is 100 °C in celsius and 212 °F.
How Boiling takes place?
Boiling is the opposite process to condensation and is natural insofar as the sequence of states in which matter can appear as the liquid and gaseous ordered sequentially.
The fundamental explanation of the process has to do with the fact that in the liquid state, the molecules move constantly and are united to each other by attractive forces.
The molecules collide with each other, and the warming of the environment makes this agitation take place in a faster and more intense way: precisely the escape of the molecules outside the same mass to be lost in the atmosphere is the transformation to the gaseous form.
Boiling temperature
The point at which this phenomenon occurs is called the boiling temperature, and it is different for each element: in some, even at a temperature below zero degrees Celsius, this evaporation can occur.
This critical point, however, is directly associated with the atmospheric pressure conditions at which it occurs, since its definition can be said to be the point at which the vapor pressure equals the external atmospheric pressure.
See Also: Difference between evaporation and boiling
Types of Boiling
- Nucleate boiling is the type of boiling, that occurs when the surface temperature is more hotter than the saturated fluid temperature by a certain limit.
- Transition boiling is defined as the unstable boiling, which takes place at the surface temperatures between the max attainable in nucleate and the minimum attainable in the film boiling.
- Film boiling occurs when a surface heating the liquid is significantly hotter than a liquid, where a thin layer of vapor, which has low thermal conductivity, insulates the surface. This condition of a vapor film insulating the surface from the liquid characterizes film boiling.
- Critical heat flux describes the thermal limit of a process where the phase change takes place during heating, which suddenly decreases the efficiency of the heat transfer.
Examples of Boiling
Here are some examples of the boiling process, detailing the temperature at which it occurs in each element:
- The boiling point of water is 100 ° C.
- The boiling point of silver, 2212 ° C.
- Neon boiles at -246 ° C.
- Nitrogen boils at -196 ° C.
- The lowest boiling point is that of helium, which at -269 ° C will already be in a gaseous state.
- Cesium boiling, at 678 ° C.
- The boiling of titanium occurs when it reaches 3287 ° C.
- The boiling point of manganese, at 1962 ° C.
- Bromine boils at 59 ° C.
- Aluminum boils at 2467 ° C.
- The carbon has a very high boiling point which is 4827 ° C.
- Boron boiling, which occurs at 2550 ° C.
- Cobalt boils, at 2870 ° C.
- The boiling of alcohol, at 78 ° C.
- Gold boiling point, at 2807 ° C.
- Phosphorus boiling, produced when 280 ° C is reached.
See Also: Types of thermometers
Standard Boiling points of Different elements:

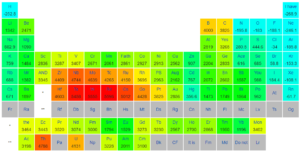
Factors affecting on boiling
1: Pressure
The greatest determinant of the boiling point of a liquid is the surrounding pressure. In an open system, the external pressure is most likely the earth’s atmosphere. Water, for example, reaches standard atmospheric pressure at 100 degrees Celsius. This measurement is taken at sea level, where the total weight of the Earth’s atmosphere presses on the water. As the elevation increases, the water may boil at a lower temperature. At the top of Mount Everest, the water boils at about 72 degrees Celsius.
2: Intermolecular Bonds
When we consider other liquids, more factors help determine the boiling point. Chief among them is the strength of the bonds between the molecules. Ethyl alcohol, for example, has a boiling point of 78.5 degrees Celsius at sea level. It is a liquid at room temperature and the bonds between its molecules are comparatively strong. In contrast, methyl ether has a “boiling” point of -25 degrees Celsius. At room temperature and sea level, methyl ether is a gas.
3: Solute, Solvents and Solutions
An effective way to raise the boiling point of a liquid is to add another ingredient. While sea-level water has a boiling point of 100 degrees Celsius, its boiling point can be increased by adding a solute, such as salt. A solvent is any substance in which another dissolves. The substance that dissolves is called the solute. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, a solution is created. A solution generally boils higher than the pure solvent.
Uses of Boiling
- Refrigeration and air conditioning
- For making water potable
- In cooking
Related Topics:
External References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boiling
- https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-boiling-604389
- https://www.britannica.com/science/boiling-point
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…