Conditions of equilibrium with examples
There are two conditions of equilibrium, the first condition of equilibrium, and the second condition of equilibrium. According to the First condition of equilibrium sum of forces acting on a body is zero ( ∑ F =0 ), While according to the second condition of equilibrium sum of torque acting on a body is zero ( ∑ τ = 0 ).
What is the equilibrium in physics?
“A body is said to be in equilibrium if no net force acts on it.”Newton’s first law of motion tells us that a body continues its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line if no resultant or net force acts on it. For example, a book lying on a table or a picture hanging on a wall is at rest. The weight of the book acting downward is balanced by the upward reaction of the table.
In the case of objects moving with uniform velocity, the resultant force acting on a leveled road and an airplane flying in the air with uniform velocity are examples of bodies in equilibrium.
What are the Conditions for a body to be in equilibrium?
In the above examples, we see that a body at rest or in uniform motion is in equilibrium if the resultant force acting on it is zero. For a body in equilibrium, it must satisfy certain conditions. There are two conditions for a body to be in equilibrium.
First condition of equilibrium
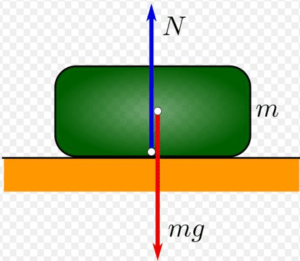


A body is said to satisfy the first condition for equilibrium if the resultant of all the forces acting on it is zero. Let n number of forces F1, F2, F3,……, Fn is acting on a body such that:
F1 +F2+F3+……+Fn =0
or ∑ F =0 ……(1)
The symbol ∑ is a Greek letter called sigma used for summation. Equation (1) is called the first condition of equilibrium.
The first condition for equilibrium can also be stated in terms of X and Y components of the forces acting on the body as:
F1x +F2x+F3x+……+Fnx =0
And
F1y+F2y+F3y+……+Fny=0
or
∑ Fx =0
∑ Fy=0
First condition of equilibrium examples
- A book lying on a table
- A picture hanging on a wall, are at rest and thus satisfies the first condition for equilibrium.
- A paratrooper coming down with terminal velocity also satisfies the first condition for equilibrium and is thus in equilibrium.
Second condition of equilibrium
If the body is not in equilibrium although the first condition for equilibrium is still satisfied. It is because the body has the tendency to rotate. This situation demands another condition in addition to the first condition for equilibrium. According to this, a body satisfies the second condition for equilibrium when the resultant torque acting on it is zero. Mathematically:
∑ τ =0
Second condition of equilibrium examples
- The force applying on the steering of the car
- Couple
- Children playing on the sea saw
Conditions of equilibrium in mechanics(video)
Related topics:
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…
View Comments
Mechanics