Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis

The main differences between mitosis and meiosis are in the number of daughter cells formed and the number of chromosomes they have.
The difference between mitosis and meiosis lies in the fact that, although they are cell division processes, they generate a different number of daughter cells, which also have a different number of chromosomes.
In mitosis, daughter cells have the same amount of genetic material as the parent cell, unlike meiosis. In mitosis, we still see the formation of two daughter cells; already in meiosis, four. In addition to all these differences, mitosis and meiosis also differ in terms of the stages of the division process and the role they play in the organism.
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of cell division that forms two daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is related, in plants and animals, with the development of organisms, healing and growth.
The stages of mitosis are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. At the end of telophase, cytokinesis occurs, that is, the division of the cell’s cytoplasm, generating two daughter cells. It is worth noting that these steps vary from one author to another. Prometaphase, for example, is not described by all authors.
Stages of mitosis
- Prophase: begins shortly after interphase, a long stage in which cell growth, organelle production, and chromosome duplication occur. In prophase, the chromosomes increase their condensation, and the nucleolus, where ribosomes are formed, disappears. The formation of the mitotic spindle (structure made up of microtubules) also begins, and the centrosomes (the region where the microtubules are organized) move away.
- Prometaphase: Disintegration of the nuclear envelope. Microtubules departing from the centrosome attach to the kinetochore (protein structure located at the centromere) of the chromosomes. The chromosomes continue their condensation.
- Metaphase: The chromosomes reach their greatest degree of condensation. The centrosomes are on opposite sides of the cell, and the chromosomes are arranged in the middle region of the cell (metaphase plate).
- Anaphase: In the shortest phase of the process of mitosis, sister chromatids separate and migrate toward the poles of the cells. The cell elongates, and at the end of this step, we have two poles with the full amount of chromosomes.
- Telophase: New nuclei and nuclear envelopes form. The nucleolus reappears, and the chromosomes become less condensed. Normally, at the end of this stage, cytokinesis occurs, which is nothing more than the division of the cell in two.
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is a cell division process that generates four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. This division process is responsible for the formation of gametes . It is essential that the gametes have half the number of chromosomes of the species, because, in this way, at the time of fertilization, the number of chromosomes of the species will be restored.
Meiosis is characterized by two processes of cell division: meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, we have prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I. In meiosis II, we have prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II.
Difference between mitosis and meiosis in tabular form
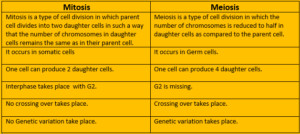
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Mitosis is a type of cell division in which parent cell divides into two daughter cells in such a way that the number of chromosomes in daughter cells remains the same as in their parent cell. | Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the number of chromosomes is reduced to half in daughter cells as compared to the parent cell. |
| It occurs in somatic cells | It occurs in Germ cells. |
| One cell can produce 2 daughter cells. | One cell can produce 4 daughter cells. |
| Interphase takes place with G2. | G2 is missing.
|
| No crossing over takes place. | Crossing over takes place.
|
| No Genetic variation takes place. | The genetic variation takes place. |
MEIOSIS I
Conclusion:
General summary
By summarizing the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans, we say that the end result of mitosis is two cells equal to 46 chromosomes (pairs of 23), and in the case of meiosis, there are four cells with 23 chromosomes each (without pairs). , in addition to the fact that its genetic material can be altered by mutation between homologous chromosomes.
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…