what is Difference between motional and induced emf?

The difference between motional and induced emf is provided here. Click here to learn brief differences between motional emf and induced emf.
This post also includes:
- Motional emf definition
- The formula of motional emf
- Induced emf definition
- Lot’s more
Let’s Dive right in…
What is Motional EMF?
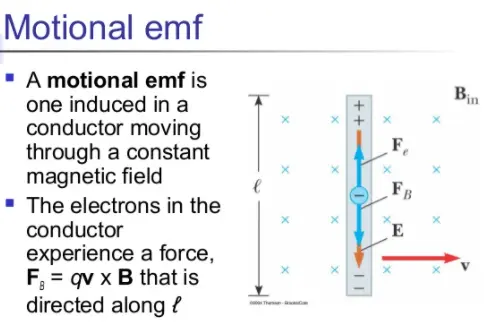
“The emf induced by the motion of a conductor across a magnetic field is called motional emf”.
In the previous section we have studied that when a conductor is moved across a magnetic field, an emf induced between its ends. The emf of the moving conductor is similar to that of a battery,i.e., if the ends of the conductor are joined by a wire to make a closed circuit, a current flow through it.
Motional emf formula
Consider a conducting rod of length L placed on two parallel metal rails separated by a distance L. A galvanometer is connected between the ends c and d of the rails. This forms a complete conducting loop abcd. A uniform magnetic field B is applied directed into the paper. Initially,
When the rod is stationary, the galvanometer indicates no current loop. If the rod is pulled to the right with constant velocity v, the galvanometer indicates a current flowing through the loop. Obviously, the current is induced due to the motion of the conducting rod across the magnetic field. The moving rod is acting as a source E =Vb –Va = ∆V.
When the rod moves, a charge q within the rod also moves with the same velocity v in the magnetic field B and the experiences a force given by
F =qv × B
The magnitude of the force is:
F = qv B sinθ
Since angle θ between v and B is 90°, so
F = q vB
Applying the right-hand rule, we see that F is directed from a to b in the rod. This suggests a uniform electric field E is induced along the rod. Its magnitude is given by:
E =F/q
substituting F =q v B in equation E=F/q,we have:
E =qvB/q
E =vB ……..(1)
The direction of electric intensity is that of force F i.e., it is directed from a to b. As the electric intensity is given by negative of the potential gradient, therefore
E = -ΔV/L
E=-ε/L ………..(2)
Comparing equation (1) and (2) we get:
-ε/L =vB
ε =-vBL ………..(3)
This is the magnitude of motional emf. However, if the angle between v and B is θ, then
ε =vBL sinθ ……….(4)
Read Also: Coulomb’s law
Motional emf equation
The above equation shows that when v=0,∑=0, that means no motional emf is developed in the stationary rod. It is also obvious that by increasing the speed of rod and using a stronger field, emf can be increased.
Due to induced emf, positive charges would flow along the path , therefore the induced current is anticlockwise the diagram.
Motional emf Vs induced emf video
See also:
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…
View Comments
The men, whose average age was 60, were additionally discovered to
have low testosterone levels during their assessment,
and 1,200 of them started testosterone therapy after their tests.