What are the Different types of electric motor?

An electric motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Basically, there are three types of electric motor, AC motors ( Synchronous and Asynchronous motors), DC motors ( brushed and brushless ), and Special purpose motors.
What is the working principle of an electric motor?
- When a current-carrying conductor is located in an external magnetic field perpendicular to the conductor, the conductor experiences a force perpendicular to itself and to the external magnetic field.
- The right-hand rule for force on a conductor can be used to determine the direction of the force experienced on the conductor: if the right thumb points in the direction of the current in the conductor and the fingers of the force on the conductor is directed outward from the palm of the right hand.
- Analog electric meters (i.e., galvanometer, ammeter, voltmeter) operate on the motor principle. Electric motors are an important application of the motor principle.
Construction
An electric motor consists of a permanent external field magnet (stator) and a coiled conducting ammeter (rotor) which is free to rotate within the field magnet. Brushes and a commutator (designed differently if A.C. or D.C. current is supplied to the armature) connect to the armature to an external voltage source. The speed of rotation of a motor depends on the amount of current flowing through it, the number of coils on the armature, the strength of the field magnet, the permeability of the armature, and the mechanical load connected to the shaft.
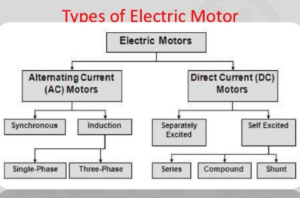
Types of electric Motor
In general electric motors are classified into two types (AC motors and DC motors).
Now!
We learn in detail about subtypes of AC motors and DC motors.
Types of AC motors
Synchronous Motors
There are two types of synchronous motors.
- Plain
- Super
Asynchronous Motors
-
Induction Motors
- Squirrel Cage
- Slip-Ring
-
Commutator Motors
- Series
- Compensated
- Shunt
- Repulsion
- Repulsion-start induction
- Repulsion induction
Classification Based On Type of Current
- Single Phase
- Three Phase
Classification Based On Speed of Operation
- Constant Speed.
- Variable Speed.
- Adjustable Speed.
Classification Based On Structural Features
- Open
- Enclosed
- Semi-enclosed
- Ventilated
- Pipe-ventilated
- Riveted frame-eye etc
Types of DC Motors
Most common DC motor types are-
- Permanent-magnet motors
- Brushed DC Motor
- DC shunt-wound motor
- DC series-wound motor
- DC compound motor
- Cumulative compound
- Differentially compound
- Permanent magnet DC motor
- Separately excited
- Brushless DC Motor
- Coreless or ironless DC motors
- Printed armature or pancake DC motors
- Universal motors
DC Motor
In general, DC motors are most desirable in two situations. The first is when the only power available is DC, which occurs in automobiles and small battery-powered devices. The other is when a torque-speed curve needs to be carefully doctored. As technology and manipulation advances in AC motors, this becomes a less important aspect, but historically the DC motor has been easy to configure making it good for servo and traction applications.
With high current and low voltage relative speed. The variations of the standard DC motor are the power, and the brushless DC motor, which is a highly complex device compared to the standard motor. DC motors are used in applications requiring velocity or position control and when a high starting torque is a need as AC motors have difficulty in this area.
Watch also:
Permanent-Magnet (PM) Motors
- The permanent magnet (PM) motor differs from the wound-field DC motor in one respect: the PM motor gets its field from a permanent magnet, whereas in the wound-field DC motor, the field is created when the field current flows through the field coils.
- In the wound-field motor, the flux is constant only as long as the field current is held constant. But in contrast, in the PM motor, the flux is always constant.
- The power produced by any motor is given by:
Where, P° = output power (in hp)
T= Torque (in Ib – ft)
Nrt = rotor speed (in r/min)
- The output power is thus proportional to the product of torque and speed.
Permanent magnet motors can be divided into 3 types:
- Conventional PM Motor
- Moving Coil Motor
- Brushless DC Motor
Conventional PM Motor
Conventional permanent magnet electric motors include a rotor assembly having pole permanent magnets bonded to a rotor hub and contained within a non-magnetic metal sleeve. Conventional rotor assemblies have included a non-magnetic material such as example plastic between each of the permanent magnets to maintain a desired orientation of the permanent magnets on the rotor hub. An interference fit between the metal sleeve and permanents magnets tightly against the rotor.
Moving Coil Rotor
The moving-coil motor (MCM), although still a PM motor, differs from the conventional PM motor primary in the armature. The MCM is a result of an engineering requirement that motors have high torque, low rotor inertia, and low electrical time constant. These requirements are met in the MCM.
Torque Motor
A case may be made that all motors produced torque. All motors could, therefore, be called torque motors. However, a torque motor is different from more other DC motors in that it is required to run for long periods in a stalled or low-speed condition. Not all DC motors are designed for this operation. A low emf means that a large amount of armature current will flow. Most conventional DC motors are not designed to dissipate the heat this large current will create. But torque motors are designed to be run under a low speed or a stalled condition for long periods of time and are used in such applications as spooling or tape drives. In spooling applications, the tension is often controlled by a torque motor.
Stepper Motor
- A stepper motor is a truly digital motor.
- After the rotor makes a step it stops until it receives a pulse.
- A stepper motor is an electromechanical device which converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements.
- The shaft or spindle of a stepper motor rotates in discrete step increments when electrical command pulses are applied to it in the proper sequence.
- The motor’s rotation has several direct relationships to these applied input pulses.
- The sequence of the applied pulses is directly related to the direction of motor shaft rotation. The speed of the motor shafts rotation is directed related to the frequency of the input pulses and the length of rotation is directly related to the number of input pulses applied.
Related topics
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…
View Comments
VERY GOOD CONTENT. BUT CAN YOU PLEASE TELL SOMETHING MORE ABOUT SYCNRONUS MOTOR AND RELAYS.
Thanks for finally talking about > Types Of Electric Motors and their Applications < Liked it!