Different types of resistors with pictures,function and uses

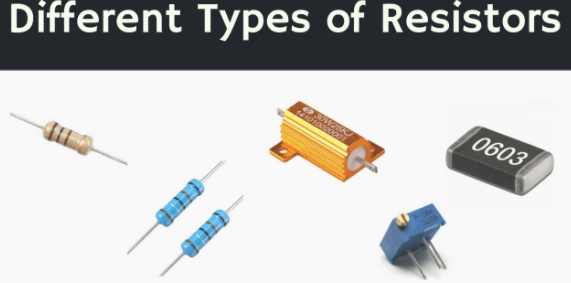
A resistor is an electrical component with a known specific value of resistance. It is probably the most common component in all kinds of electronic equipment ranging from a small radio to a color television receiver. Fixed Resistors and Variable resistors are the two main types of resistors.
As its name suggests, a resister resists or opposes the flow of current through it. Resistance is necessary for any circuit to do useful work. In fact, without resistance, every circuit would be a short circuit!
Uses of resistors
Some of the common uses of resistors are:
- to establish proper values of circuit voltage due to IR drops
- to limit current and
- to provide load
The two main characteristics of a resister are its resistance and power rating. Resistors can be connected in the circuit in either direction because they have no ‘polarity’.
Types of resistors and their applications
Resistors are mainly of two types and can be either of the fixed or variable value.
- Wire wound resistor
- Carbon resistors
- Carbon composition type
- Carbon film type
- Cermet film type
- Metal film resistors
Another type is called a metal thin film resistor.
Wire wound resistors
They are constructed from a long fine wire(usually nickel-chromium wire) wound on a ceramic core. The length of the wire used and its resistivity determines the resistance of the unit. The wire is bare but the entire assembly is covered or coated with a ceramic material or special vitreous enamel.
Such resistors are generally available in power ratings from 5 W to several hundred watts and resistance values from 1 Ω to 100 k. These can be of either a fixed value or variable type. Wire wound resistors are used where:
(a): Large power dissipation is necessary
(b): Precise and stable resistance values are required for meter shunts and multipliers
Carbon composition Resistors
They are made of finely divided carbon mixed with a powered insulating material in suitable proportion. Often, the resistance element is a simple rod of press carbon granules which is usually enclosed in a plastic case for insulation and mechanical strength. The two ends of the carbon resistance element are joined to metal caps with leads of tinned wire for soldering its connections into a circuit.
Such resistors are available in power ratings of 1/10,1/8,1/4,1/2,1,2 watt and in resistance values ranging from 1 Ω to 20 MΩ. Where power dissipation is 2 W or less, such resistors are preferred because they are smaller and cost less . Carbon resistors with a power rating of 1 W or less are most common in electronic equipment.
Carbon film resistors
They consist of a high-grade ceramic rod or core (called the substrate) on which is deposited a thin resistive film of carbon. They are cheaper than composition resistors.
Cermet film resistors
They consist of a thin carbon coating fired on to a solid ceramic substrate. The main purpose is to have more precise resistance values and greater stability with heat. Very often, they are made in a small square with leads to fit into a printed circuit board.
Metal film Resistors
They are also referred to as thin-film resistors. They consist of a thin metal coating deposited on cylindrical insulating support. The high resistance values are due to the thinness of the film. Because it is difficult to produce films of uniform thickness, it is not possible to control their resistance values accurately as in the case of wire wound resistors. Such resistors are free of troublesome inductance effects so common in wire wound resistors, particularly at high frequencies.
Power Ratings of resistors
The power rating of a resistor is given by the maximum wattage it can dissipate without excessive heat. Since it is current which produces heat, power rating also gives some indication of the maximum current a resistor can safely carry. If the current exceeds this value, more heat will be produced than can be carried safely and the resistor will burn out, A 1/2 watt resistor, for example, can dissipate 1/2 watt of heat without damage various a 1 W resistor can throw off twice as much heat. In a circuit, you may substitute a 1-watt resistor of the same resistance value for a 1/2 watt resistor but not vice versa.
The physical size of a resistor is no indication of its resistance through it thus give some indication of its wattage rating. For a given value of resistance, the greater the physical size, the higher the power rating. Also, higher wattage resistors can operate at higher temperatures, moreover, a higher power rating allows a higher voltage rating. This rating gives at the highest voltage that may be applied across the resistor without internal arcing.
Value tolerance:
BY tolerance is meant the possible variations from the nominal or marked resistance value of a resistor. It means that actual resistance of the resistor may be greater or lesser than its indicated value. All resistors are manufactured and sold with a specified tolerance. For example, a 1000 Ω resistor with a tolerance of 10 % will have an actual resistance anywhere between 900 Ω and 1100 Ω i.e 100Ω more or less than the rated value.
Carbon composition resistors have tolerance of ±5%,±10 %, and ± 20 % whereas general purpose wire wound resistors usually have a tolerance of ± 5%.
How does a variable resistor work?
Variable resistors are designed so that their resistance values can be changed easily with a manual or an automatic adjustment. Two basic uses for variable resistors are to divide voltage is called a potentiometer.
The variable resistor used to control current is called a rheostat.
For related Topics Visit Our Page: Electronics
Recent Posts
Difference between Gastritis and ulcer
Gastritis and ulcers are irritations, which must be treated urgently in order not to develop…
Saudi Arabia launches new residency plans to draw foreign talent
On Thursday, Saudi Arabia unveiled fresh residency programs geared towards drawing in skilled professionals and…
Study in UAE: Your Complete Guide to Enrolling Abroad
Studying abroad can be a life-changing experience, opening doors to new cultures, perspectives, and opportunities.…
Difference between Osmosis and dialysis
The difference between osmosis and dialysis is that Osmosis is a physical phenomenon by…
Difference between Vitamins and proteins
The Difference between Vitamins and Proteins is given here. Vitamins and proteins are essential…
Difference between Windows and Linux
The Difference between Windows and Linux is given here. Windows and Linux are operating systems…
View Comments
Hello. remarkable job. I did not expect this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
thank you very much dear, i hope this blog will help further help you ahead, thanks for watching,apriciatting and for every thing
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that I have really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again very soon!
vAD5Ta Incredible! This blog looks just like my old one! It as on a completely different subject but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Great choice of colors!
"Fantastic post.Really thank you! Great."
.}
Fantastic. Just what I needed to support a litigation I am involved in.
you are welcome Dr.Andrew.
You explained very well.
thank you, dear.