Symptoms of Thyroid



The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It plays a crucial role in regulating various metabolic processes in the body by producing hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) These hormones influence metabolism, growth, and energy expenditure.
Causes of thyroid enlargement
Thyroid disorders can arise due to various causes, with the most common being autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis leads to an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) as the immune system attacks the thyroid tissue, impairing hormone production. On the contrary, Graves’ disease results in an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) due to the immune system stimulating excess hormone production.
Examples:
Examples of other causes include iodine deficiency, certain medications, radiation therapy, and congenital thyroid abnormalities. Additionally, thyroid nodules or tumors can disrupt normal thyroid function, contributing to disorders.
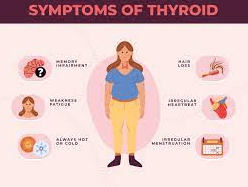
Symptoms of Thyroid
Symptoms of thyroid dysfunction vary depending on whether the gland is overactive or underactive. it include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, and depression. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism may present with symptoms like weight loss, increased heart rate, anxiety, tremors, and heat intolerance.
1. Hypothyroidism ( Muscles Weakness and Joint Pain)
Individuals with hypothyroidism may experience muscle weakness and joint pain due to reduced metabolism affecting the musculoskeletal system.
2. Menstrual Irregularities:
Women with an underactive thyroid may encounter changes in their menstrual cycle, such as heavier or irregular periods.
In managing thyroid disorders, diagnosis often involves blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Treatment options may include medication to regulate hormone levels, radioactive iodine therapy, or, in severe cases, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.
3.Constipation:
Slowed digestive processes are common in hypothyroidism, leading to symptoms like constipation.
4. Hair Loss:
Thinning hair or hair loss can be a noticeable symptom of an underactive thyroid.
Mood Swings and 5.Mood swings and Anxiety:
Thyroid disorders can impact mental health, contributing to mood swings, anxiety, and even depression.
5.Swelling in the Neck (Goiter):
Enlargement of the thyroid gland, known as a goiter, can occur in both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Healthy lifestyle:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, exercise, and managing stress, can positively impact thyroid health. Regular monitoring and collaboration with healthcare professionals are essential for effective management of thyroid disorders.
Conclusions:
In conclusion, the thyroid gland is a vital component of the endocrine system, influencing various bodily functions. Understanding the causes and symptoms of thyroid disorders is crucial for early detection and appropriate intervention, ensuring individuals can lead healthy lives despite these challenges.
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…