Mechanics
Mechanics for physics is the branch of physics that deals with the study of the motion of objects, its causes and effects. Basically there are three types and branches of mechanics, classical mechanics, and quantum mechanics.
Classical mechanics deals with the study of macroscopic objects while classical mechanics deals with the study of microscopic objects.
Kinematics, statics, and dynamics are further types of classical mechanics.
Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that deals with the study of the motion of objects without discussing its cause.
Dynamics is the study of the motion of objects, and its causes and effects are called dynamics.
In mechanics we will learn in detail about the following topics:
Mechanics
Kinematics
speed
velocity
acceleration
kinematic equations
different types of motion in physics with examples
projectile motion equations
Difference between speed and velocity
Dynamics
Types of forces
newton’s laws of motion
Newton’s first law of motion examples
Newton’s second law of motion examples
Newton’s third law of motion examples
Law of conservation of momentum with examples
types of friction
Gravitation
gravity
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion
Work & Energy
forms of energy
kinetic energy examples
potential energy examples
work energy theorem derivation
energy sources
renewable energy sources
solar energy
work definition in physics
Turning Effect of Forces
turning effect of forces
states of equilibrium
conditions of equilibrium
Collisions
Collision and its types
Difference between elastic and inelastic collision
Fluid dynamics
Fluid mechanics
Equation of continuity derivation
Bernoulli Equation derivation and applications
viscosity and its applications
pressure in liquids formula
pascal law formula and its applications
archimedes principle and law of floatation
Special Theory of Relativity postulates
Exploring space
benefits of Space exploration\
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of space that we can assign…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base quantities or fundamental quantities are…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest or of uniform motion in…
Difference Between Micrometer Screw Gauge and Vernier Caliper
The basic difference between screw gauge and vernier caliper is that screw gauge is used to measure only external measurement…
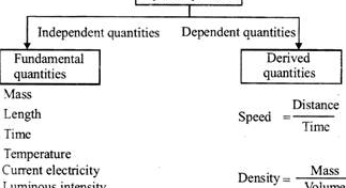
Types of Physical Quantities
Physical quantities are those quantities that can be measured. Basically, there are two types of physical quantities (Base quantities or…
Types of Simple machines with examples and Applications
Simple machines are devices that allow changing the intensity or the direction of the energy reaching their point of entry…
What is The International System of Units?
In 1960, an international committee agreed on a set of definitions and standards to describe the physical quantities. The system…
Difference between young’s modulus, bulk modulus and shear modulus
The basic difference between young's modulus, bulk modulus, and shear modulus is that Young's modulus is the ratio of tensile…
difference between centre of mass and centre of gravity in tabular form
The basic difference between centre of mass and centre of gravity is that Center of mass is a point in…
States of Matter and their properties for kids
The matter is everything that occupies space and has a size and mass that can be measured. Solids, liquids, gas,…