Applications of Pascal law
Pascal law states Pressure applied at any point of a liquid enclosed in a container is transmitted without loss to all other parts of the liquid. Hydraulic press, Hydraulic jack system, and brake system are a few applications of Pascal law.
Pascal law formula
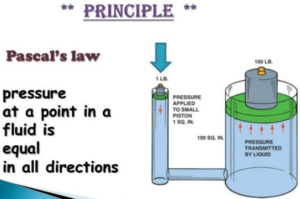
It can be demonstrated with the help of the glass vessel having holes all over its surface. Fill it with water. Push the piston. The water rushes out of the holes in the vessel with the same pressure. The force applied to the piston exerts pressure on the water. This pressure is transmitted equally throughout the liquid in all directions.
In general, this law holds good for fluids both liquids as well as gases.
Pascal’s principle examples in real life
Pascal’s law finds numerous examples in our daily life such as :
- automobiles
- hydraulic brake system
- hydraulic jack
- hydraulic press
- hydraulic machines.
Applications of pascal’s law

- Hydraulic press
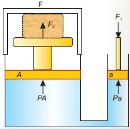
The hydraulic press is a machine that works on Pascal’s law. It consists of two cylinders of different cross-sectional areas. They have fitted with pistons of cross-sectional areas a and A. The object to be compressed is placed over the piston of a large cross-sectional area A. The force F1 is applied to the piston of the small cross-sectional area a. The pressure P produced by the small piston is transmitted equally to the large piston and a force F2 acts on A which is much larger than F1.
Press on the piston of the small area a is given by :
P =F1/a
Apply pascal’s law, the pressure on the large piston of area A will be the same as on the small piston.
- P =F2/A
Comparing the above equations, we get:
F2/A= F1/a
Hence:
F2= A ×F1/a
OR
F2 = F1 ×A/a
Since the ratio is greater than 1, hence the force F2 that acts on the larger piston is greater than the force F1 acting on the smaller piston. Hydraulic systems working in this way are known as force multipliers.
The braking system in Vehicles
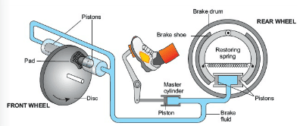
The braking systems of cars, buses, etc. also work on pascal’s law. The hydraulic brakes allow equal pressure to be transmitted throughout the liquid. When the brake pedal is pushed, it exerts a force on the master cylinder, which increases the liquid pressure in it. The liquid pressure is transmitted equally through the liquid in the metal pipes to all the pistons of the other cylinders. Due to the increase in liquid pressure, the pistons in the cylinders move outward pressing the brake pads with the brake drums. The force of friction between the brake pads and the brake drums stops the wheels.
Hydraulic lift
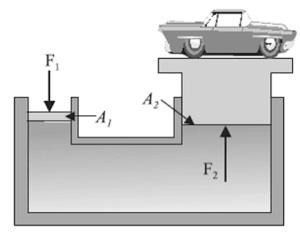
In a hydraulic lift, a narrow cylinder A is connected with a wider cylinder B and they are fitted with airtight pistons. It is filled with some incompressible fluid. Pressure can be applied to move the piston in cylinder A in the downward direction.
The pressure so applied is transmitted according to pascal’s principle to the piston of cylinder B. Consequently, the piston B moves upward in a hydraulic lift the piston B is used as a platform for a car or any heavier object to be lifted, like a truck, car, also in playland, etc.
Watch also the video:
Related topics
- Archimedes principle
- Continuity equation
- Bernoulli equationhttps://oxscience.com/continuity-equation/
- Viscosity
External source:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal%27s_law

[email protected]