Difference between Cation and Anion

A cation is an ion that has a positive charge and an anion is an ion that has a negative charge. Both cations and anions are types of ions. An ion is an atom or group of atoms that have an electrical charge, that is, they have a difference between the number of protons and the number of electrons that make it up.
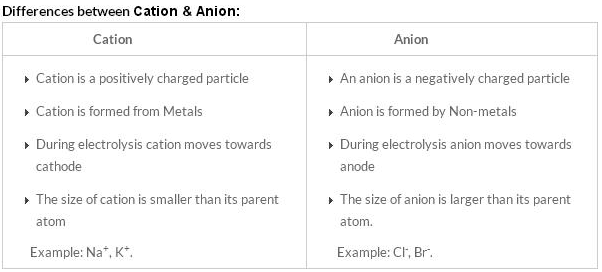
Difference between Anion and Cation in tabular form
| Difference | cations | anions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | positively charged ion | negatively charged ion |
| Training | It is formed by loss of electrons | It is formed by gaining electrons |
| Burden | Positive charge | negative charge |
| types of ions |
|
|
| examples |
|
|
What is an anion?
An anion in chemistry is defined as an ion that is negatively charged because it has excess electrons.
How is an anion formed?
An anion is formed when it gains electrons, that is, it gains one or more negative charges.
10 Examples of anions
Here is a list of the different types of anions.
Monovalent monatomic anions: ions of a single atom with a negative charge
- Chloride anion Cl-
- Fluoride anion F –
- Bromide anion Br –
- Iodide anion I –
- Hydride anion H –
Divalent monatomic anions: ions of a single atom with two negative charges
- Sulfide anion S 2-
- Oxide anion O 2-
Trivalent monatomic anions: ions of a single atom with three negative charges
- Nitride anion N 3-
- Phosphide anion P 3-
- Arsenide anion As 3-
polyatomic anions: ions of two or more atoms
- Peroxide anion O 2 2-
- Arsenate anion AsO 4 3-
- Borate anion BO 3 3-
- Bromate anion BrO 3 –
- carbonate anion CO 3 2-
- Bicarbonate anion HCO 3 –
- hypochlorite anion ClO –
- Chlorite anion ClO 2 –
- Chlorate anion ClO 3 –
- Perchlorate anion ClO 4 –
- Cyanide anion CN –
- Amide anion NH 2 –
- OCN cyanate anion –
- SCN thiocyanate anion –
- Hydroxide anion OH –
- Permanganate anion MnO 4 –
- Sulfate anion SO 4 2-
- Sulfite anion SO 3 2-
- Nitrate anion NO 3 –
- Nitrite anion NO 2 –
- Phosphate anion PO 4 3-
- Acetate anion C 2 H 3 O 2 –
- Thiosulfate anion S 2 O 3 2-
What is a cation?
A cation in chemistry is defined as an ion that is positively charged because it has lost electrons from its outermost shell.
How is a cation formed?
Cations form when they lose one or more electrons from their valence shell.
Examples of the most common cations
Here is a list of different types of cations.
Monovalent monatomic cations: ions of a single atom with a positive charge
- Lithium cation Li +
- Sodium cation Na +
- Potassium cation K +
- Silver cation Ag +
- Copper (I) cation Cu +
Divalent monatomic cations: ions of a single atom with two positive charges
- Beryllium cation Be 2+
- Calcium cation Ca 2+
- Magnesium cation Mg 2+
- Strontium cation Sr 2+
- Barium cation Ba Ba 2+
- Zinc cation Zn 2+
- Chromium (II) cation Cr 2+
- Manganese(II) cation Mn 2+
- Iron(II) cation Fe 2+
- Cobalt(II) cation Co 2+
- Copper (II) cation Cu 2+
- Lead(II) cation Pb 2+
Trivalent monatomic cations: ions of a single atom with three positive charges
- Aluminum cation Al 3+
- Chromium (III) cation Cr 3+
- Manganese(III) cation Mn 3+
- Iron (III) cation Fe 3+
- Cobalt(III) cation Co 3+
Polyatomic cations: ions of two or more positively charged atoms.
- Mercury (I) cation Hg 2 2+
- Ammonium cation NH 4 +
- Hydronium cation H 3 O +
You may be interested in seeing:
- Atoms and Molecules.
- Differences between acids and bases.
Read Also:
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…