Conduction of heat Transfer Examples

What is conduction of heat?
Conduction Of heat transfer is the transfer of internal energy by microscopic collisions of the particles and the movement of free electrons within a body. Colliding particles, which contain molecules, atoms, and electrons, transfer kinetic energy and P.E, together called internal energy. Conduction of heat takes place in all phases of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
This post includes:
- Conduction of heat transfer definition
- Examples of conduction of heat
- Applications
- Lot’s more
Let’s dive right now…
The rate at which energy is conducted as the heat between two bodies depends on the temperature difference between the two bodies which are in contact with each other.
The heat automatically flows from a hotter body to a colder body. For example, heat flows from the hot plate of a stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it.
In the process of conduction of heat, the heat flows within and through the object itself. On the other hand, in heat transfer by the thermal radiation, the heat transfer is often between bodies, which may be separated spatially.
In convection heat transfer, the internal energy flows between bodies by moving material carriers. In the solids, conduction is carried out by the combination of collisions and vibration of molecules.
In gases and liquids, conduction occurs due to collisions of molecules during their irregular motion.
See Also: Difference between Heat and Temperature
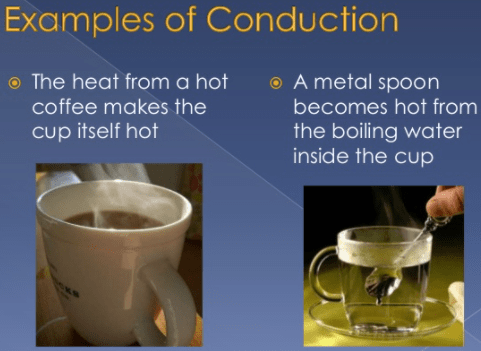
Examples of Conduction of Heat Transfer
Here are some examples of conduction of Heat:
- Utensils used to handle charcoal or other very hot substances. Keep in mind that the extension is long so that the heat transfer is slower.
- The ice, when put in a cup of boiling water, melts completely.
- When you bring water to a boil, the gas stove flame transmits the heat to the pot, and from one moment to the next the water is already heated.
- The heat that comes from a kitchen utensil when you leave it on a container and turn over it a soup that is practically burning.
Heat conduction in solids
In solids, atoms and molecules are packed close together. They continue to vibrate about their mean position. What happens when one of its ends is heated? The atoms or molecules present at that end begin to vibrate more rapidly. They also collide with their neighboring atoms or molecules. In doing so, they pass some of their energy to neighboring atoms or molecules during collisions with them will increase in their vibrations. These atoms or molecules intern pass on a part of the energy to their neighboring particles. In this way, some heat reaches the other parts of the solids. This is a slow process and a very small transfer of heat takes place from hot to cold parts in solids.
How do metals differ from non-metals in terms of conducting heat?
Metals have free electrons. These free electrons move with very high velocities within the metal objects. They carry energy at a very fast rate from hot to cold parts of the object as they move. Thus, heat reaches the cold parts of the metal objects from their hard parts much more quickly than nonmetals.
All metals are good conductors of heat. The substances through which heat does not conduct easily are called bad conductors or insulators. Wood,cork,cotton,wool,glass,rubber,etc are bad conductors or insulators.
See Also: Difference between conductors and insulators
Examples of conductive materials
| Pure silver | Gallium |
| Hardened copper (**) | Nickel |
| Aluminum | Graphite |
| Pure zinc | Tantalum |
| Phosphor bronze | Bronze |
| Nickel | Steel |
| Brass | Galvanized metal |
| Tungsten | Iron |
| Cast iron | Copper |
| Gold | Ionized air |
Applications of conduction of heat in our daily life
Use of good conductors of heat
- Cooking utensils, saucepans, kettles and boilers are made of metals where direct heating is involved.
- Soldering iron is made of iron with a tip made of copper because copper is a much better conductor of heat than iron.
Use of insulators or bad conductors
Some common applications of insulators are given:
- Handles of kettles and spoons are made of plastic or wood because wood is the poor conductor of heat. In this way, the hot kettles, utensils, and spoons can be picked up without burning our hands.
- Woolen clothes or blankets are used to keep people warm on cold days.
- Sawdust is used to cover up ice blocks because it has good insulating properties.
Related Topics:
convection heat transfer
Radiation heat transfer
Difference between conduction convection and radiation
Difference between Conductors and Insulators
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…