5 Examples of Convection

In this post, you’ll learn the Convection of Heat and Examples of Convection.
If You want to get Benefits from this Post, You’ll love this Post.
Contents:
- Convection Definition
- Examples
- Applications
- Lot’s More…
Keep Reading…
W
Transfer of heat by the actual movement of molecules from a hot place to a cold place is known as convection. Sea breezes, land breezes, and convection currents are a few examples of convection. Convection occurs only in liquids and gas.
Liquids and gases are poor conductors of heat. However, heat is transferred through fluids (liquids or gases)easily by another method called convection.
Why does a balloon inflate with the hot shown in the figure .rise up? a liquid or a gas becomes lighter (less dense) as it expands on heating. Hot liquid or gas rises up above the heated area. The cooler liquid or gas from the surroundings fills the places which in turn is heated up.in this way, all the fluid is heated up. Therefore, the transfer of heat through fluids takes place by the actual movement of heated molecules from hot to cold parts of the fluid.
Convection of heat in liquids
Unlike particles of solids, particles in liquids and gases move from one place to another. Take a beaker and put small pieces of paper in it.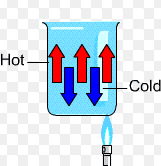
Fill half of the beaker with water. Heat the beaker by a spirit lamp. We shall see that pieces of the paper rise to the top of the water, move sideways, and sink to the bottom. The water in the beaker also gets warm. The molecules of water absorb heat energy from the bottom of the beaker and rise to the top. Other surroundings molecules of water come to the bottom to absorb heat energy. From the above experiment, we can also define convection as: “The transfer of heat in which molecules of a medium actually move to the source of heat energy to absorb heat and then move away from it, is called convection.”
Is Convection occurs in solids?
Convection occurs in liquids and gases only because their molecules can move freely. The molecules of a solid are held closely together. They cannot move freely. The molecules of a solid are held closely together. They cannot move freely, therefore, convection is not possible in solids.
What is the difference between a land breeze and sea breeze?
Land Breeze:
Land and sea breezes are the result of convection. On a hot day, the temperature of the land increases more quickly than the sea. It is because the specific heat of land is much smaller as compared to water. The air above the land gets hot and rises up. cold air from the sea begins to move toward the land. It is called a sea breeze.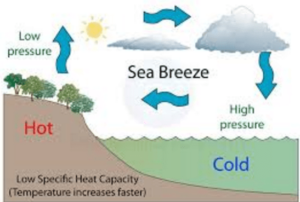
Sea Breeze:
At night, the land cools faster than the sea. Therefore, the air above the sea is warmer, rises up and the cold air from the land begins to move towards the sea as illustrated .it is called a sea breeze.
GLIDING:
What causes a glider to remain in the air?
A glider such as looks like a small airplane without an engine. Glider pilots use the upward movement of hot air currents due to the convection of heat. These rising currents of hot air are called thermals. glider ride over these thermal. The upward movement of air currents in thermal helps them to stay in the air for a long period.
How do thermals help birds to fly for hours without flapping their wings?
The birds stretch out their wings and circle in these thermals. The upward movement of air helps birds to climb up with it. Eagles, hawks, and vultures are expert thermal climbers. After getting the free lift, birds are able to fly for hours without flapping their wings. They glide from one thermal to another and thus travel through large distances and hardly need to flap their wings.
Examples of convection
- A water pump in a house, where the hot water is divided for effective distribution of the same, passes through a means (the pump) so that it goes out to the shower and the person can bathe with the required amount.
- Home ovens use convection technology so that the person can modulate the temperature level they want when cooking food that is cold. Internally, a stream of hot air will circulate.
- Convection occurs at the bottom of the oceans where the energy of the water meets the surface that is cold, and results in ocean currents.
- When a volcano is erupting it is because the force of gravity has attracted its hot fluids to the surface, the rest of the fluids descend.
- Convection stoves transfer heat causing a completely innate circulation of air and this causes heat to spread evenly throughout the site.
- The hot air balloons are sustained in the air thanks to the hot air emanating from the engine, but if they cool down, the balloons begin to collapse.
- When a person is bathing in very hot water, the glass in the shower fogs up.
- The hairdryer has a motor that serves as a fan to force air through a hot resistor. Therefore, it transmits heat by forced convection.
Applications of convection
The household water system is based on convection. It works as:
Water is heated in the boiler by gas burners. The hot water expands and becomes less dense. Hence it rises and flows into the upper half of the cylinder.
To replace the hot water, cold water from the cistern falls into the lower half of the cylinder and then into the boiler due to pressure difference.
The overflow pipe is attached to the cylinder just in case the temperature of the water becomes too high and causes a large expansion of the hot water.
The hot-water tap which is led from the overflow pipe must be lower than the cistern so that the pressure difference between the cistern and the tap causes the water to flow out of the tap.
- Electric Kettles
The heating coil of an electric kettle is always placed at the bottom of the kettle.
When power is switched on, the water near the heating coil gets heated up, expand,s and becomes less dense. The heated water, therefore, rises while the cooler regions in the upper part of the body of the water descend to replace the heated water.
- Air Conditioners
The rotary fan inside the air-conditioner forces cools dry air out in the room. The cool air, being dense, sinks while the warm air below, being less dense, rises and is drawn into the air conditioner where it is cooled. In this way, the air is recirculated and the temperature of the air falls to the value preset on the thermostat.
- Refrigerators
Refrigerators work in very much the same way as air conditioners. The freezing unit is placed at the top to cool air, being dense. Sinks while the warm air at the bottom rises. This sets up convection currents inside the cabinet which help to cool the contents inside.
Learn more about convection watch video:
Browse:

“Is Convection occurs in solids?” Not to be *that* person, but it should be “does Convection occur in solids” or “can Convection occur in solids.” Consider checking all of your grammar, please, before posting something on the internet for someone to use as a resource.