Kinematic Equations in Physics List

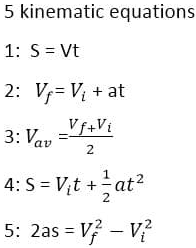
Kinematics is the branch of mechanics dealing with the motion of bodies without reference to mass or force. There are three kinematic equations in Physics for bodies moving with uniform acceleration. These equations relate initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration, time, and distance covered by a moving body.
For equations of motion derivation, we assume that the motion is along a straight line. Hence, we consider only the magnitude of displacements, velocities, and acceleration.
List of Kinematic Equations in Physics
The first equation of motion derivation by graphical method
Consider a body moving with initial velocity Vi in a straight line with uniform acceleration a. Its velocity becomes Vf after time t. The motion of the body is described by the speed-time graph represented by line AB. The slope of line AB is acceleration a. The total distance covered by the body is shown by the shaded area under the line AB. Kinematic equations of motion can be obtained easily from this graph.
Speed time graph for the motion of a body is shown in the figure. The slope of line AB gives the acceleration of a body.
See Also: Newton laws of motion
The second equation of motion derivation by graphical method
Consider a body is moving with initial velocity ‘Vi’ in a straight line with uniform acceleration ‘a’.Lets its velocity becomes ‘Vf’ after time t. The motion of the body is described by the speed-time graph by line AB as shown in the figure below. The total distance ‘S’ is covered by the body is equal to the total area OABD under the graph.
It is known as the 2nd equation of motion.
Third (3rd) equation of motion by graphical method
Consider a body moving with initial velocity ‘vi’ in a straight line with uniform acceleration ‘a’.Let its velocity becomes Vf after time ‘t’.The motion of the body is described by the speed-time graph as shown in the figure by line AB. The total distance ‘S’traveled by the body is given by the total area OABD under the graph.
It is 3rd equation of motion.
The conditions under which these equations can be applied:
1: Motion should be 1-dimensional.
2: Acceleration should be uniform.
3: Frame of reference should be inertial.
Related topics:
- velocity
- acceleration formula
- kinematic equations
- different types of motion in physics with examples
- projectile motion equations
- Difference between speed and velocity
- Difference between uniform and non uniform motion
- Third equation of motion derivation by graphical method
- Value of acceleration due to gravity
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…
View Comments
Remove the adds please
why dear?