Metallic Bond Examples

Metallic bonds are a type of chemical bond that occurs between atoms of the same metal. Through these links, very compact structures are achieved, since the nuclei of the atoms come together so much that they begin to share their valence electrons. For example bonds between aluminum atoms.
These valence electrons remain around the set of nuclei as in a kind of cloud and the attraction between their negative charges and the positive charges of the nuclei is what holds the set firmly together.
In this way, the metallic bond is a strong and primary atomic bond, which can only occur between atoms of the same species and never as a form of the alloy ( mixture of metals). Nor should this type of bond be confused with ionic or covalent bonds, although it may share certain aspects with the latter since the atoms involved share their electrons to a certain extent.
Metallic bond Properties
The main characteristics or Properties of Metallic bonds are given in the list below:
- They exhibit electrostatic attraction because they are non-directional.
- They have a high metallic bond strength that is proportional to the cation charge.
- The interaction of the metal’s electrons with different wavelengths gives them a metallic gleam.
- Electrical power is transmitted through them.
- When electrons are heated, they gain a tremendous amount of kinetic energy and are able to migrate to cooler regions.
- They have energy dissipation and cation vibration characteristics when the shock happens.
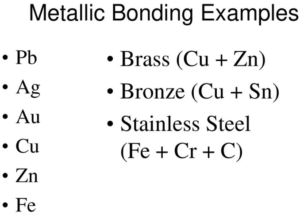
Metallic bond Examples list
Metallic bonds are extremely common in the atomic world of metals, so any pure metallic element is a possible example:
- Bonds between silver (Ag) atoms.
- Bonds between gold (Au) atoms.
- Bonds between cadmium (Cd) atoms.
- Bonds between iron (Fe) atoms.
- Bonds between nickel atoms (Ni).
- Bonds between zinc atoms (Zn).
- Bonds between copper atoms (Cu).
- Bonds between platinum (Pt) atoms.
- Bonds between aluminum atoms (Al).
- Bonds between gallium (Ga) atoms.
- Bonds between titanium atoms (Ti).
- Bonds between palladium (Pd) atoms.
- Bonds between lead atoms (Pb).
- Bonds between iridium (Ir) atoms.
- Bonds between cobalt (Co) atoms.
Related Post
Recent Posts
Is energy quantized in classical physics?
No, according to classical wave theory the emission of electromagnetic radiations from the surface is…
Types of laser
Basically, there are four types of laser which includes: Gas Lasers Solid State lasers Liquid…
Ultrasound frequency range
What is ultrasonics? The study and application of mechanical vibrations with frequencies beyond the limits…
Electromagnetic Energy: What are some examples of it?
Electromagnetic energy definition Electromagnetic energy is the amount of energy stored in a region of…
Fundamental units and Derived Units with Examples
The Main Difference between fundamental Units and Base units is that Units that Express base…
Newton’s First law of Motion Examples in Our Daily Life
Newton's first law of motion states that " A body continues its state of rest…