Difference between polar and non polar dielectric materials
Dielectrics are insulating materials through which the electric current cannot pass easily, because these materials have a very high value of electrical resistance. For example, paper, pyrex, polystyrene, transformer oil, pure water, silicon, etc.
Types of Dielectric materials
There are two types of dielectrics:
- Polar Dielectrics
- Non-polar dielectrics
Polar dielectrics
The dielectric materials which have permanent electric dipoles moment ‘p’ are called polar dielectrics. These materials consist of molecules that are permanent dipoles.
In the absence of an external electric field, the polar molecules are randomly oriented. As a result, these materials have no net dipole moment.
When the external electric field is applied, then all dipoles tend to align themselves with the external electric field. But the thermal agitation tends to keep the dipoles randomly oriented. Hence the partial alignment of electric dipoles is produced in a polar dielectric medium for specific field strength. However, the alignment of dipoles can be increased by increasing the external electric field and decreasing the temperature.
Non polar dielectrics
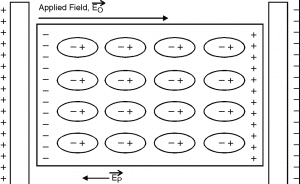
The electric materials which don’t have permanent dipole moments are called nonpolar dielectrics. In the absence of an external electric field, the atoms are neutral. When the electric field of strength ‘E0‘ is applied, then it tends to separate positive and negative charges on the atoms of molecules. As a result, the atoms and molecules of dielectric become dipoles called induced dipoles, and this process is called electric polarization.
If the non-polar dielectric materials are placed in an electric field having strength ‘E0‘ then another electric field ‘E’ is produced due to polarization of the medium. The electric field produced due to the polarization of the dielectric is always opposite to the direction of the external electric field. So, the net electric field in the region is ‘E=E0-E’. Hence,the net electric field is reduced due to the polarization of the dielectric medium.
Capacitance with dielectric formula
Consider a parallel plate capacitor that is connected with a battery of emf ‘V’.Let ‘A’ is the area of each plate and is the separation between the plates.
If ‘q’ charge is stored in the capacitor when there is a vacuum or air as a medium between the plates, then:
q= CV
Where ‘C’ is the capacitance of the capacitor, which, in the case of a parallel plate capacitor is expressed as:
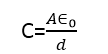
Michael Faraday, in 1937, investigated that if the space between the plates of the parallel plate capacitor is filled with some dielectric medium, then the charge stored in the capacitor increased to ‘q’.And hence, the capacitance of the capacitance also increases to ‘C’.
Effect of Dielectric on capacitance formula
When there is no dielectric medium between the plates of the capacitor, the stored charge ‘q’ in the capacitor can find out using the expression:
q=CV
But when the dielectric medium is placed between the plates of the capacitor, then the net electric field and the net potential difference between the plates are reduced due to the electric polarization of the dielectric medium. Therefore, the battery does work to transfer more charges to increase the potential difference between the plates. Therefore, more charge is stored in the capacitor, when a dielectric medium is placed between its plates and hence the capacitance of the capacitor increased.
Watch also video: