Convection Current Examples and Applications
In this post, You’ll Learn Applications and Examples of Convection currents, which is the Example of Convection of Heat.
If You want to Get Benefits From this Post, you’ll love this Post.
What you’ll learn…..
Keep Reading…..
What is convection Current?
Gasses expand on heating thus convection currents are easily set up due to the difference of densities of air at various parts in the atmosphere. Or The upward and downward movement of molecules of water or air is called a convection current. convection currents occur on a large scale in nature. The day _to_day temperature changes in the atmosphere result from the circulation of warm or cold air that travels across the regions, land, and sea breezes are also Convection current Examples.
What is Atmospheric Convection?
Atmospheric convection plays a fundamental role in determining global climate patterns and in our daily weather variations. Gliders pilots and condors alike seek the convection thermals that, rising from the warmer Earth beneath, keep them aloft. Huge energy transfers take place within the oceans by the same process. The outer region of the sun, called the stratosphere, contains a vast array of convection cells that transport energy to the solar surface and give the surface a granulated appearance.
Different types of convection currents
We know that convection is the transfer of heat by the actual movement of the particles in materials. Winds and ocean currents are examples of the effects of convection.
Wind current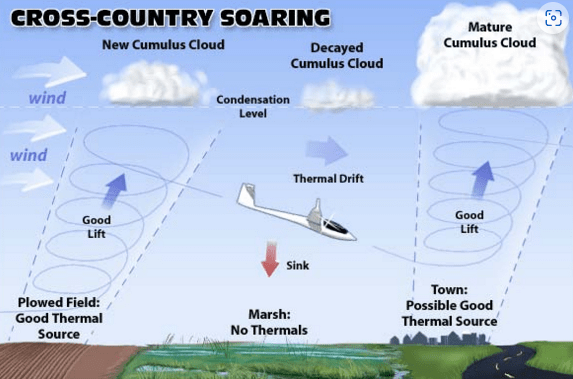
The heat of the sun heats up the surface of the Earth and the air near it also gets hot. The air expands and gets lighter. So, it rises up and cool air from the neighboring regions moves in to fill its space. The rising warm air reaches the upper colder layers of the air and cools down. Cool heavy air sinks to the Earth in cold regions to blow again to take the place of the rising air. Thus, convection currents are set up, and the wind system goes on.
Ocean Currents
ocean currents are also set up due to the convection of heat. The water in the hot regions of an ocean gets hot, expands, and gets lighter, but water in the colder regions remains cold and heavy. hot water moves along the surface of the ocean towards the colder regions. The cold water flows below the surface of the ocean towards the hot regions.in this way, ocean currents are set up.
What is Gliding Flights of Birds?
Convection currents also take place in the atmosphere. The heat from the Sun warms the air near the ground. The warm air expands and becomes lighter in weight. As warm air rises, colder air rushes in to fill its place near the ground. This process continues. Birds like eagles, hawks, vultures, and gulls advantage of this phenomenon. They enjoy gliding. During gliding flight, a bird does not move its wings but glides on air currents. A lot of energy of birds saved during gliding.
Application of Convection Currents
We can observe the use of convection currents in our surroundings.
- Household ventilation can make our house cool. The air which we breathe out is warmer and lighter. It moves up in the room to go out of the ventilators near the top side of the walls. Fresh and cool air enters the room through windows and doors.
- In a domestic water heater, water is heated in the boiler by a gas burner or heating coil. the hot water expands and becomes lighter in weight. this water rises and flows into the upper part of the water heater. To take the place of hot water, cold water from the storage tank (cistern) falls to the lower part of the water heater to be hot. We take the hot water from the tap attached to the water heater, convection currents help in the continuous supply of the water.
- An air conditioner also uses convection currents to cool a room. Air conditioners are installed near to be the ceiling. The rotary fan of an air conditioner releases cool dry air. The cool air is heavier in weight, so it sinks. the warm air of the room rises because it becomes lighter in weight. The air conditioner draws this warm air to make it cool. In this way, the air circulates again and again, and the desired temperature is gained.
Related topics in our site are:
