Image formation by convex and concave lens ray diagrams
How convex and concave lens work?
In mirrors, images are formed through reflection but lenses form images through refraction. This is explained with the help of ray diagrams as follows:
Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams
Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in the figure.
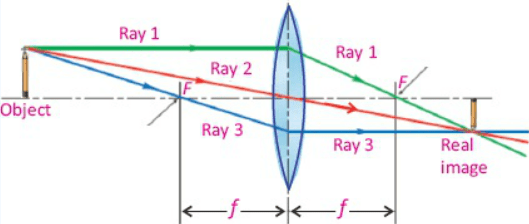
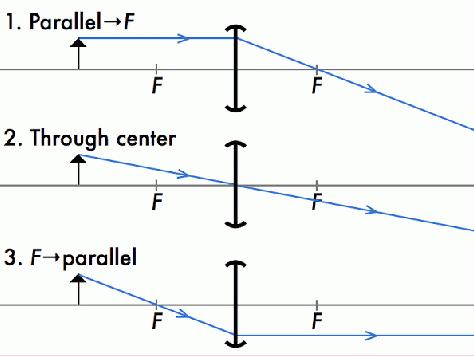
- The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens.
- The ray passing through optical centre passes straight through the lens and remains undeviated.
- The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens.
 \
\
- The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens.
Ray diagram for concave lens
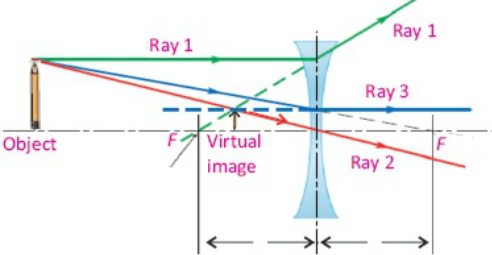
Image formation in convex lens
Case 1:When object beyond 2F:
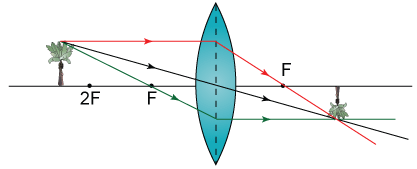
In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object.
Case 2:When object is placed at 2F
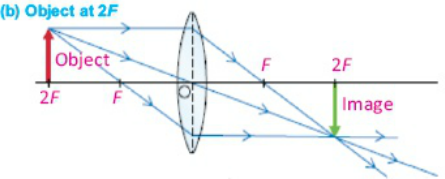
In this case image will form at 2F, also image will be real , inverted, the same as the size of the object.
Case 3:When object is placed between F and 2F
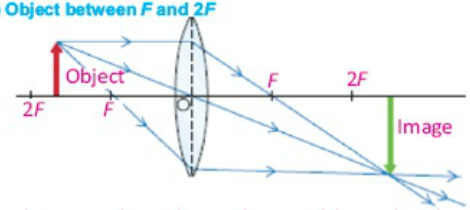
In this case image will form beyond the 2F,also image will be real, inverted, larger than the object.
Case 4:When object is placed at F:

In this case no image will formed because the refracted rays are parallel and never meet.
Case 5:When object is placed between F and optical center
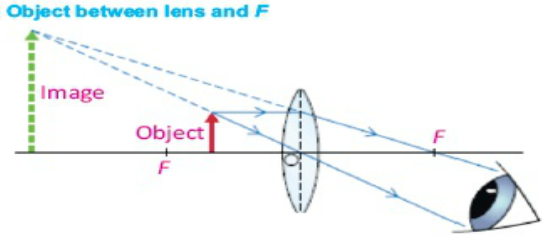
In this case image will form behind the object, also image will be virtual, erect, larger than the object.
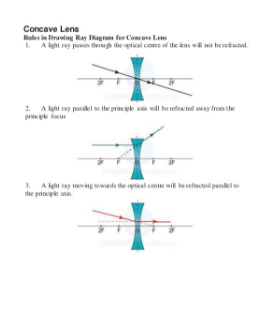
Image formation by concave lens ray diagrams
Suggested Video:

Hello,nice share.
You overcome suffering, it is your wealth; suffering overcomes you, it is your humiliation