What is nuclear reactor?How does it works ?
In a nuclear power station, the reactor plays the same part as does furnace in a thermal power station. In a furnace, coal or oil is burnt to produce heat, while in a reactor fission reaction produces heat. When fission takes place in the atom of uranium or another heavy atom, then energy at the rate of 200 MeV per nucleon is produced.
This energy appears in the form of the kinetic energy of the fission fragments. These fast-moving fragments besides colliding with one another also collide with the uranium atom. In this way, their kinetic energy gets transformed into heat energy. This heat produces steam which in turn rotates the turbine. The turbine rotates the generator which produces electricity. A sketch of a power station is shown in figure:
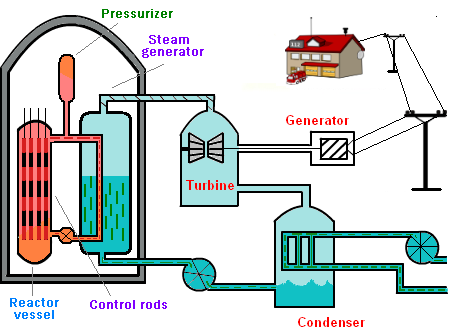
Nuclear reactor components
- The most important and vital part of a reactor is called the core. Here the fuel is kept in the shape of cylindrical tubes. Reactor fuels are of various types. Uranium was used as fuel in the elementary reactors. In this fuel, the quality of
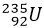 is increased from 2 to 4 percent. It may be remembered that the quality of in the naturally occurring is only 0.7 percent. Now-a-day plutonium-239 and uranium-233 are also being used as fuel.
is increased from 2 to 4 percent. It may be remembered that the quality of in the naturally occurring is only 0.7 percent. Now-a-day plutonium-239 and uranium-233 are also being used as fuel. - The fuel rods are placed in a substance or small atomic weight, such as water, heavy water, carbon or hydrocarbon, etc. These substances are called moderators. The friction of these moderators is to slow down the speed of the neutrons produced during the fission process and to direct them toward the fuel. Heavy water, if may be remembered is made of
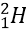 , a heavy isotope of hydrogen instead of
, a heavy isotope of hydrogen instead of 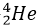 . The neutrons produced in the fission reaction are very fast and energetic and are not suitable for producing fission in reactor fuel like
. The neutrons produced in the fission reaction are very fast and energetic and are not suitable for producing fission in reactor fuel like  or
or 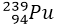 etc. For this purpose, slow neutrons are more useful. To achieve this moderators are used.
etc. For this purpose, slow neutrons are more useful. To achieve this moderators are used. - Besides moderator three in an arrangement for the control of a number of neutrons, so that all the neutrons produced are fission, only one neutron produces further fission reaction. The process is achieved either by cadmium or by boron because they have the property of absorbing fast neutrons. The control rods made of cadmium or boron are moved in or out of the reactor core to control the neutrons that can initiate the further reaction. In this way, the speed of the chain reaction is kept under control. In case of emergency or for repair purposes control rods are allowed to fall back into the reactor and thus stop the chain reaction and shut down the reactor.
- Heat is produced due to a chain reaction taking place in the core of the reactor. The temperature of the core, therefore, rises to about 1200 °C. To produce steam from this heat, it is transported to a heat exchanger with the help of water, heavy water, or any other liquid under great pressure. In the heat exchanger, this heat is used to produce steam from ordinary water. The steam is then used to run the turbine which in turn rotates the generator to produce electricity. The temperature of the steam coming out of the turbine is about 300°C. This is further cooled to convert it into the water again. To cool this steam, water from some river or sea is, generally, used. Heavy water is being used as a moderator and for the transportation of heat also from the reactor core to the heat exchanger, heavy is used. To cool steam coming out of the turbine seawater is being used.
Read Also: Nuclear Reactions
The nuclear fuel once used for changing the reactor can keep on operation continuously for a new month. Thereafter the fissile material begins to decrease. Now the used fuel is removed and fresh fuel is fed instead. In the used up fuel is an intensely radioactive substance. The half-life of this radioactive remnant material is many thousand years. The radiations and the particles emitted out of this nuclear waste are very injurious and harmful to living things.
Unfortunately, there is no proper arrangement for the disposal of nuclear waste. This cannot be dumped into oceans or left in any place where they will contaminate the environment, such as through the soil or the air. They must be not allowed to get into the drinking water. The best place so far found to store these in the bottom of old salt mines, which are very dry and are thousands of meters below the surface of the Earth. Here they can remain and decay without polluting the environment.