What is Ohm’s law class 10?

Ohm’s law states that: “The current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends provided the physical state such as temperature etc. of the conductor remains constant.”The formula for ohm’s law is “V=IR”.
Ohm describes mathematically how voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit are related. It is used in the equivalent form depending on which quantity you need to determine. In this section, you will learn each of these forms.
Relationship between voltage and current
Ohm determined experimentally that if the voltage across a resistor is increased, the current through the resistor will also increase; and, likewise, if the voltage is decreased, the current will decrease. For example, if the voltage is doubled, the current will double. If the voltage is halved, the current will also be halved.
V ∝ I
Relationship between current and resistance
Ohm law also states that if the voltage is kept constant, less resistance results in more current, and, also, more resistance in less current. For example, if the resistance is halved, the current doubles. If the resistance is doubled, the current is halved.
I ∝ 1/R
Ohm’s law formula
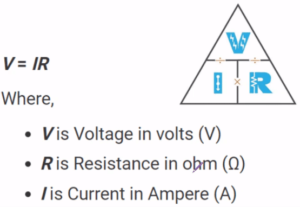
V=IR
Where R, the constant of proportionality is called the resistance of the conductor. The value of the resistance depends upon the nature, dimensions, and physical state of the conductor. V has applied voltage in volts and I is current in amperes.
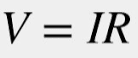
Equation (1) is the ohm law equation in which “V” is voltage “I” is the current and “R” is the resistance.
difference between ohmic and non-ohmic conductors
Conductors that obey ohm’s law are called ohmic conductors in other words materials whose resistance is constant are called ohmic conductors.
Ohmic conductor examples
Metals mostly are ohmic conductors, their resistance remains constant by increasing voltage current and temperature. Current-voltage graphs of these materials show a straight line. Some of the examples of ohmic conductors are:
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Silver
- Iron
These are examples of ohmic conductors.
Non-ohmic conductors
Conductors or materials which do not obey ohm’s law of ohm are called non-ohmic conductors or materials. or The conductors whose resistance increase or decreases by increasing voltage current and temperature. Their voltage-current graph shows not a straight line.
Non-ohmic conductors examples
- Electric bulb filament
- Thermister
- Semiconductor diodes
- LDR
- Transistors
- Lighting arrester
- Heater
Ohm law practice problems
In the following examples, the formula I=V/R is used. In order to get current in amperes, you must express the value of voltage and the value of resistance in ohms.
Example: Calculate the current in the following figure.
solution: In the above figure R=10 KΩ and V=50 V then from ohm’s law:
V=IR
I=V/R
I=50V/10 KΩ
I=5mA
Calculating voltage using ohmic law
We can find voltage by using the relation of ohm’s law V=IR if we know the current and resistance of a circuit.
Example: Find voltage if the current of 5mA is flowing through the following circuit.
In the above figure R=10KΩ, I=5mA, by using ohm’s relation V=IR:
V=(5mA)(10KΩ)
V=50V
Lets see video about ohm law.Stay with us: