Difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
The basic difference between prokaryotes and Eukaryotes is that in prokaryotic cells DNA arrangement is Circular while in Eukaryotic cells DNA arrangement is linear. More Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells are given below in detail.
Keep reading …
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells are the most diverse cells, as well as the simplest and oldest if we look at the evolutionary history of living organisms. Its very name, from the Greek “pro” which means “before”, refers to its existence prior to the appearance of the other type of existing cells, eukaryotes.
Characteristics of Prokaryotic cells
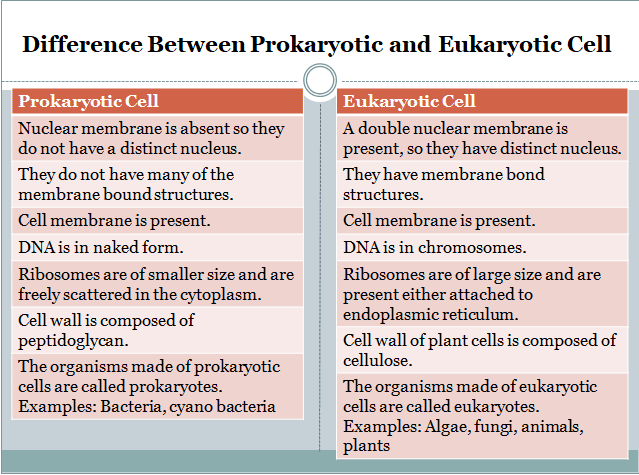
- In prokaryotes, the Nuclear membrane is absent so they do not have a distinct nucleus.
- They do not have many membrane-bound structures.
- The cell membrane is present.
- DNA is in naked form.
- Ribosomes are of smaller size and are freely scattered in the cytoplasm.
- The cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan or mucin.
- cellulose is absent.
- The organisms made of prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes
Examples of Prokaryotic cells
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- archaea
- blue algae
- green algae
What is a eukaryotic cell?
The meaning of eukaryote comes from Greek, where “EU” means “true” and “karyon” means “nucleus”. In this way, the main characteristic that defines eukaryotic cells is the presence of a true nucleus inside their cellular structure, which delimits and maintains the cell’s DNA in an organized way.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells
- A double nuclear membrane is present so they have a distinct nucleus.
- They have membrane-bound structures.
- The cell membrane is resent.
- DNA is in chromosomes.
- Ribosomes are of large size and are present either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or freely suspended in the cytoplasm.
- The cell wall of plant cells is composed of cellulose.
- Cellulose is present.
- The Organisms made up of Eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes.
Examples of Eukaryotic Cells
Common Examples of eukaryotes are:
- Algae
- fungi
- animals
- plants
- protozoans
Difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in tabular form
| Prokaryotic Cell
| Eukaryotic Cell | |
| Cell Type | Organisms made up of prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes.
| Organisms made up of eukaryotic cells are called Eukaryotes. |
| Cell size | The average diameter of 1 – 10 um.
| Mostly 10 – 100 um in diameter. |
| Form of Organisms | They are Unicellular. | They are unicellular and Multicellular, truly multicellular. |
| Nucleus | No well-defined Nucleus is present. | A well-defined Nucleus is present. |
| Genetic System |
DNA is in suspended form. |
DNA is within Nucleus. |
| Ribosomes | Smaller Ribosomes. | Larger Ribosomes. |
| Cell Division | The cell divides by binary fission. | Cell devides by Mitosis & Meiosis. |
Similarities Between Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic Cells
Apart from the differences seen, there are also some similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells :
- Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are the basic and fundamental units of life on Earth. Thanks to them, each and every one of the different unicellular and multicellular organisms has been able to evolve and colonize the different habitats of the planet.
- Both types of cells are characterized by structures delimited by membranes that in their interior conserve their DNA or genetic information, as well as different enzymatic machinery that allows them to carry out their vital functions: feeding, growth, and reproduction.
- In order to survive and evolve, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells constantly convert energy from one form to another, in addition to maintaining a continuous relationship with their exterior, in order to respond to the different sources of chemical-biological information they receive from the environment.
Conclusion: Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells membrane do not have cholesterol while Eukaryotic cell membranes have cholesterol.
Related Articles: