7 Branches of Physics with Examples
The branch of science which deals with the interaction of matter and energy is called physics. There are Two Main Branches of Physics, Classical Physics, and Modern Physics. Further sub Physics branches are Mechanics, Electromagnetism, Thermodynamics, Optics, etc.
The rapid progress in science during recent years has become possible due to discoveries and inventions in the field of physics. The technologies of our modern society throughout the world are related to physics. For example, a car is made on the principle of mechanics, and a refrigerator is based on the principles of thermodynamics.
Importance of physics in our daily life
In our daily life, we hardly find a device in which laws of physics are not involved.
Examples
- Pulleys are used to lift heavy loads.
- Electricity is used to get light, heat, and mechanical energy that drives fans and electric motors.
- Means of transportation such as cars and airplanes, domestic appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, vacuum cleaners, washing machines, microwave ovens, etc.
- The means of communication such as radio, TV, telephone, and computer are the result of applications of physics. These devices have made our lives much easier and faster and more comfortable than in the past.
- The computer is the invention of physics.
Branches of physics list
In the practical field, the common Types of physics are:
- Mechanics
- Classical physics
- Modern physics
- Thermodynamics
- Electricity
- Magnetism
- Geo physics
- Plasma physics
- Optics
- Sound and oscillation
- Electronics
- Chemical physics
- Engineering physics
- Solid-state physics
- Quantum physics
- Nuclear physics
- Particle physics
- Biophysics
- Astrophysics
- Condensed matter physics
10 branches of physics and their definition
Classification of physics has been done as:
Mechanics
It is the study of the motion of objects, their causes, and their effects.
Sub branches of mechanics are:
- Classical mechanics
- Kinematics
- Dynamics
- Statistical mechanics
Thermodynamics (Heat)
It is the study of the nature of heat, modes of transfer, and effects of heat.
Sound
It is the study of the physical aspects of sound waves, their production, properties, and applications.
Light(optic)
It is the study of the physical aspects of light, its properties, and the use of optical instruments.
Electricity and Magnetism
It is the study of the charges at rest and in motion, their effects, and their relationship with magnetism.
Atomic physics
It is the study of the structure and properties of atoms.
Nuclear physics
It is the study of the properties and behavior of nuclei and particles.
Plasma physics
It is the study of the production and properties of the ionic state of matter.
Geophysics
It is the study of the internal structure of the earth.
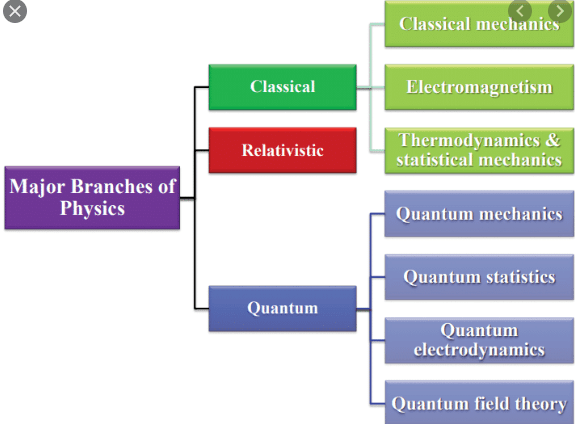
Classical physics
The branch of physics deals with newton’s laws of motion, the law of gravitation, Maxwell’s kinetic theory, and thermodynamics.
Classical physics is mostly related to energy and matter which are considered as different entities. The main branches of classical physics are Acoustics, optics, classical mechanics, and electromagnetic.
Major subtopics of classical physics
- Classical mechanics
- Electromagnetism
- Thermodynamics
Quantum physics
Major subtopics of Quantum physics
- Quantum mechanics
- Quantum statistics
- Quantum electrodynamics
- Quantum field theory
Relativistic Physics
- Special relativity
- General relativity
- Einstein field equations
Modern physics
It is the branch of physics that deals with the theory of relativity and quantum mechanics. Max Plank and Einstein are considered the father of modern physics.
Bio-Physics
Biophysics is the branch of physics in which we study biological problems and phenomena by using techniques of physics. The major application and achievement of biophysics is D.N.A.
Astrophysics
The branch of physics deals with the study of universes such as stars, planets, galaxies, etc
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of physics in which the motion of an electron is controlled by using semiconductor devices.
Chemical physics
It is the study of the science of physical relations involved in chemistry.
Engineering Physics
It is the study of the fields of physics and engineering.
Econophysics
It deals with physical processes and their relations in the science of economy.
Health Physics
It involves the protection of people who works with are near radiation.
Mathematical Physics
It is the study of mathematical systems that stands for physical phenomena.
Molecular Physics
It examines the structure, properties, and behavior of molecules.
Particle physics
It is also called high energy physics and analyses the behavior and properties of elementary particles.
These links may help You:
Handpicked links
thank you sir you people helped me very well.
Wow I love this
Have learn alot
I was in a bet about this and I had to see if i was right.I was!
Have learn alot
Good to know
Excellent
[email protected]
Thank you. This helped.
Thank you very much ? you have helped me to know what I never knew ???️????
Nice Article! Have a lot thing to learn.
Thank You this is very helpful
Thanks. I learn more
U
TRASH
k bbg~
mmk bbg~
Why is it trash?