Thermodynamics
What is thermodynamics?
Thermodynamics is one of the types of physics which is the combination of two words ” thermal + heat”, thermal means heat, and dynamic means motion. So literally thermodynamic means study of the motion of heat. There are three laws of thermodynamics which are:
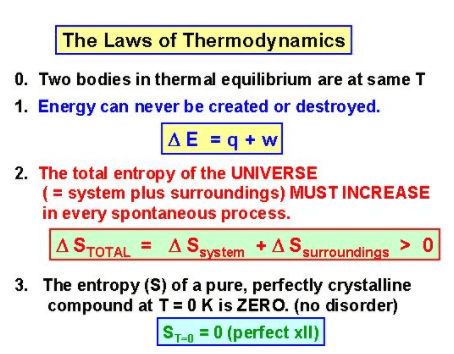
- First law of thermodynamics
- Second law of thermodynamics
- Zeroth law of Thermodynamics
Thermodynamic plays a vital role in our lives.
Think!
Without TD…..
- We were not able to get the energy to move. We get energy from food as a result of the metabolism process which is the example or application of the first law of TD.
- Refrigerators, air conditioners, cars, airplanes, buses, ships all needed a thermodynamic system to work.
- Heat pumps and heating systems are due to TD.
- Electricity is now being produced by using a thermodynamic cycle or process.
It is applicable only in the macroscopic world and not in the microscopic.
Learning Objectives
- State the Basic Postulates of the kinetic theory of gasses
- Derive gas laws on the basis of kinetic theory
- Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas
- To understand the term work and heat in thermodynamics
- Differentiate between isothermal and adiabatic processes
- Explain the molar specific heat of a gas
- Apply the first law of thermodynamics to derive Cp - Cv = R
- Explain the second law of thermodynamics and its meaning in terms of entropy
- Understand the concept of reversible and irreversible processes
- Define the term heat engine
- Understand and describe Carnot Theorem
- Describe temperature scales
- Describe the working of petrol and diesel engine
- Explain the term entropy
- Appreciate the environmental crisis as an entropy crisis.
If You want to get benefits from this easy and comprehensive guide, you’ll love this page.
Keep reading..
Temperature
Laws of thermodynamics
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Carnot engine
- Heat engine
- Internal energy Examples
- Examples of Entropy
- Reversible and Irreversible process
Heat
- Heat
- Specific Heat Capacity
- modes of Heat transfer
- Convection Examples
- Radiation Examples
- Effects of Heat: Thermal Expansion and Thermal contraction
- Thermal conductivity
- Evaporation: Definition and Examples
- Sublimation
- Condensation
- Difference between Evaporations and Boiling
- Latent Heat of Fusion And Latent heat of vaporization
- Boiling Point