What is mechanics in physics?
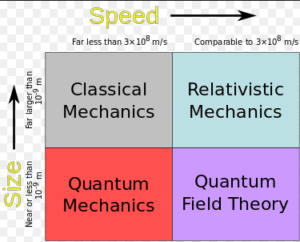
The branch of science deals with the study of the motion of the body, its causes, and its effects.
It is the oldest of the physical sciences and is the study of the motion of objects. The calculation of the path of a baseball or of a space probe sent to Mars is among its problems, as is the analysis of the tracks of elementary particles formed collisions in our largest accelerators.
Types of mechanics
- Quantum Mechanics
- classical Mechanics
- Fluid Mechanics
- Kinematics
- Dynamics
Related topics on mechanics:
- Mechanics
- Kinematics
- Dynamics
- Gravitation
- Work & Energy
- Turning Effect of Forces
- Collisions
- Fluid dynamics
- Special Theory of Relativity postulates
- Exploring space
Quantum Mechanics
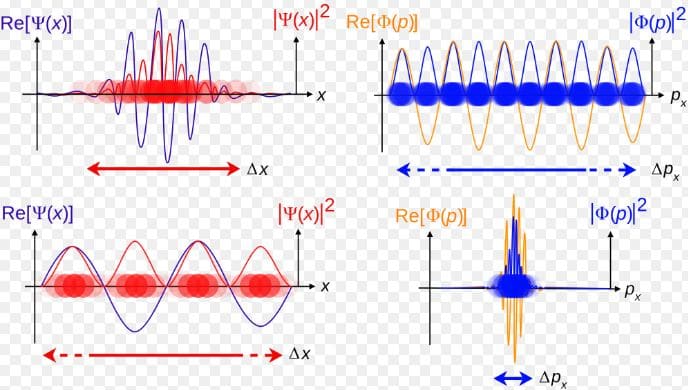
“It is the study of very tiny things.”In the early part of the twentieth century, many experimental and theoretical problems remained unresolved. Attempts to explain the behavior of matter on the atomic level with the laws of classical physics were not successful. Phenomenon such as black body radiation, the photoelectric effect, the emission of sharp spectral lines by atoms in a gas discharge tube, and invariance of the speed of light, could not be understood within the framework of classical physics. To explain these observations a revolutionary framework of explanation was necessary which we call modern physics. Its two most significant features are relativity and quantum theory. The observations on objects moving very fast, approaching the speed of light, are well explained by the special theory of relativity. Quantum theory has been able to explain the behavior of electromagnetic radiation as discrete packets of energy and the particles on a very small scale are dominated by wave properties.
Classical physics is still valid in ordinary processes of everyday life. But to explain the behavior of tiny or very fast-moving particles , we have to use the above-mentioned theories. In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of the electron behavior in a crystal when the electron is subjected to various potential functions.
The motion of large objects, such as planets and satellites, can be predicted to a high degree of accuracy using classical theoretical physics based on Newton’s laws of motion. But certain experimental results, involving electrons and high-frequency electromagnetic waves , appear to be inconsistent with classical physics. However, these experimental results can be predicted by the principles of quantum mechanics. The Quantum mechanical wave theory is the basis for the theory of semiconductor materials whose electrical properties are directly related to the behavior of electrons in the crystal lattice.
Topics of quantum mechanics
- Schrodinger wave equation
